Use a custom data source
Reveal is designed to retrieve data from Cognite Data Fusion (CDF). In certain scenarios it might be useful to customize how Reveal retrieves data, to e.g.:
- Introduce application specific caching to reduce network traffic
- Improve responsiveness in areas with limited connectivity
- Introduce extra logging of network activity related to 3D
- Store models locally
Note that certain features relies on connectivity to CDF and won't work without a connection.
Overview
To implement a custom data source, DataSource from @cognite/reveal/extensions/datasource must be implemented
and provided to Cognite3DViewer on construction using the customDataSource-option, which in turn
provides instances of three interfaces:
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
ModelMetadataProvider | Provides access to metadata about models, including "base URL", camera information and model transformation. |
ModelDataProvider | Access to geometry files and JSON description files for 3D models given URLs. |
NodesApiClient | Provides access to metadata about 3D nodes, such as bounding box and ancestors. |
Some of the interface functions are required, some are optional at the cost of reduced functionality in Reveal. See details below.
ModelMetadataProvider
ModelMetadataProvider is responsible for determining the "base URL" for a model, determine
the "model transformation" and the default camera.
Implementations can assume that all identifiers will be of type CdfModelIdentifier:
class CdfModelIdentifier implements ModelIdentifier {
readonly revealInternalId: symbol;
readonly modelFormat: File3dFormat;
readonly modelId: number; // CDF ModelID
readonly revisionId: number; // CDF RevisionID
}
| Function/Field | Required? | Description |
|---|---|---|
getModelUri() | Yes | Determine the base URL that will be used when download metadata and geometry using ModelDataProvider. |
getModelCamera() | No - return undefined to use default | Return an initial camera pose for the model |
getModelMatrix() | Yes, but value can be hardcoded. | Returns an transformation matrix for transforming from stored coordinates to Reveal coordinates (see below) |
getModelOutputs() | Yes | Returns an object describing the set of valid formats and version for the given model |
getModelUri() returns a "base URL" that will be passed to ModelDataProvider.getBinaryFile() and getJsonFile(). Note that
it's up to ModelDataProvider how this base URL is handled and it is possible to use this base URL as
some other identifier, e.g. a folder on disk or ID of a blob storage. getModelUri() accepts BlobOutputMetadata as input which
defines the format, version, and if applicable, the "blob id" of the output.
getModelMatrix() is responsible for converting from stored geometry coordinates to Reveal coordinates (right-handed, Y up). This
is required for models stored in different orientation in CDF. For CAD models, most models are stored in a right-handed Z up coordinate system, and will need
a transformation. By default, this transformation can be expressed as:
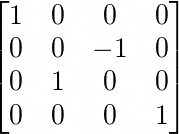
This corresponds to a 180 degree rotation around the X axis:
new THREE.Matrix4().makeRotationFromEuler(new THREE.Euler(-Math.PI / 2, 0, 0));
For point clouds, models are usually stored right-handed Y up and requires no transformation. In this case, the identity matrix should be returned instead:
new THREE.Matrix4().identity();
In addition to the model identifier, the methods can accept the format of the output which describes which output format that is used for the given model/revision.
getModelOutputs() returns a list of supported outputs for a given model/revision.
The BlobOutputMetadata type includes the format, version, and if applicable, the "blob id" of the model.
Example implementation
This simple implementation provides metadata for models stored locally and provides default camera and model transformation.
Notice that each of the functions asserts that the identifier is a CdfModelIdentifier. Currently,
this should always be true.
import {
CdfModelIdentifier,
ModelIdentifier,
ModelMetaDataProvider
} from '@cognite/reveal';
class MyModelMetaDataProvider implements ModelMetaDataProvider {
getModelUri(identifier: ModelIdentifier, formatMetadata: BlobOutputMetadata): Promise<string> {
if (!(identifier instanceof CdfModelIdentifier)) {
throw new Error('Unexpected identifier');
}
// Base URL of where geometry files are stored
// This will be passed to ModelDataProvider.getJsonFile() and getBinaryFile()
return Promise.resolve(`https://localhost/models/${identifier.modelId}/revision/${identifier.revisionId}`);
}
getModelCamera(identifier: ModelIdentifier): Promise< { position: THREE.Vector3; target: THREE.Vector3 } | undefined> {
if (!(identifier instanceof CdfModelIdentifier)) {
throw new Error('Unexpected identifier');
}
// Use default camera
return Promise.resolve(undefined);
}
getModelMatrix(identifier: ModelIdentifier, format: File3dFormat | string): Promise<THREE.Matrix4> {
if (!(identifier instanceof CdfModelIdentifier)) {
throw new Error('Unexpected identifier');
}
// CAD models are usually stored in Z-up, while Reveal uses Y-up, so
// we need to account for this
const cadModelToReveal = new THREE.Matrix4().makeRotationFromEuler(new THREE.Euler(-Math.PI / 2, 0, 0));
return Promise.resolve(cadModelToReveal);
}
getModelOutputs(modelIdentifier: ModelIdentifier): Promise<BlobOutputMetadata[]> {
// Indicates that the supported output for this model is of type File3dFormat.RevealCadModel and version 8
// BlobId refers to a remote identifier for a blob storage, but since this simply fetches
// the model locally, it can be set to -1
return Promise.resolve([
{
blobId: -1,
format: File3dFormat.RevealCadModel,
version: 8
}
]);
}
}
ModelDataProvider
ModelDataProvider is responsible for receiving files by URL.
| Function/Field | Required? | Description |
|---|---|---|
getBinaryFile() | Yes | Retrieves a binary blob. Used to download CAD geometry and point clouds |
getJsonFile() | Yes | Retrieves JSON data. This is used to retrieve metadata about models |
Example implementation
The following example simply downloads files using fetch(). Note that
it's up to the implementation to decide how to retrieve data, and that
data doesn't necessarily need to be downloaded over HTTP.
import { ModelDataProvider } from '@cognite/reveal';
class MyModelDataProvider implements ModelDataProvider {
async getJsonFile(baseUrl: string, fileName: string): Promise<any> {
const url = `${baseUrl}/${fileName}`;
const response = await fetch(url);
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`Could not fetch '${url}'`);
}
return response.json();
}
async getBinaryFile(baseUrl: string, fileName: string): Promise<ArrayBuffer> {
const url = `${baseUrl}/${fileName}`;
const response = await fetch(url);
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`Could not fetch '${url}'`);
}
return response.arrayBuffer();
}
}
NodesApiClient
The API client is responsible for providing metadata about 3D CAD nodes, including node bounding boxes and parent/child relationships between nodes.
| Function/Field | Required by (in CogniteCadModel) | Description |
|---|---|---|
mapTreeIndicesToNodeIds() | mapTreeIndexToNodeId(), mapTreeIndicesToNodeIds(), getBoundingBoxByTreeIndex() | Maps from Reveal tree indices to CDF node IDs used to identify nodes in CDF |
mapNodeIdsToTreeIndices() | No, but recommended to have a 1:1 mapping | Reverse mapping of mapTreeIndicesToNodeIds() |
determineTreeIndexAndSubtreeSizesByNodeIds() | No | Determines the "span" of a node identified by a CDF node ID (i.e. the tree index and how many descendants it has including the node itself). |
determineNodeAncestorsByNodeId() | No | Find "ancestor span" of a node identified by the CDF node ID. Returns data on same format as function above. |
getBoundingBoxesByNodeIds() | No | Determines the individual bounds of each node, specified by their CDF node IDs. |
Example implementation
class MyNodesApiClient implements NodesApiClient {
mapTreeIndicesToNodeIds(modelId: number, revisionId: number, treeIndices: number[]): Promise<number[]> {
// Map 1:1 - pretend treeIndices == nodeIds
return Promise.resolve(treeIndices);
}
mapNodeIdsToTreeIndices(modelId: number, revisionId: number, nodeIds: number[]): Promise<number[]> {
// Map 1:1 - pretend treeIndices == nodeIds
return Promise.resolve(nodeIds);
}
determineTreeIndexAndSubtreeSizesByNodeIds(modelId: number, revisionId: number, nodeIds: number[]): Promise<{treeIndex: number; subtreeSize: number }[]> {
throw new Error('Not supported.');
}
determineNodeAncestorsByNodeId(modelId: number, revisionId: number, nodeId: number, generation: number): Promise<{treeIndex: number; subtreeSize: number }> {
throw new Error('Not supported.');
}
getBoundingBoxesByNodeIds(modelId: number, revisionId: number, nodeIds: number[]): Promise<THREE.Box3[]> {
throw new Error('Not supported.');
}
}
Unsupported features
There's a few features that is not backed by the DataSource-API and hence won't be affected by the implementation. The most
notable feature is the CAD styling API which in large is backed by CogniteClient. To use the styling API with
custom data sources, you will need to create custom node collections or use TreeIndexNodeCollection.
Currently there are restrictions in the the API for saving viewer state causing Cognite3DViewer.setViewState not
to work with a custom DataSource. This might change in the future.